Preparing For the Major Changes Coming to Gmail and Yahoo Email Requirements

Navigating Upcoming Gmail and Yahoo Email Changes: What You Need to Know
In October 2023, Google and Yahoo separately announced major changes to their email delivery requirements for bulk senders (which Google defines as: “Those who send more than 5,000 messages to Gmail addresses in one day”), with both platforms set to enforce these updates in early 2024. This announcement raised several key questions for marketers across every industry:
- WHO will be affected by this update? Any business that uses an Email Service Provider to send bulk or batch emails.
- WHY is this update taking place? Gmail and Yahoo want to protect users from phishing, unwanted, and spam emails. The new requirements address this goal through two key areas: technical infrastructure and user feedback.
- WHAT TO DO to prepare for the update?: Gain a clear understanding of the updates and ensure your business stays compliant by following our checklist below.
CHECKLIST
Implement these changes by January 31, 2024 for each of your domains:
- Configure SPF email authentication
- Configure DKIM email authentication
- Configure DMARC email authentication
- Set up valid forward PTR records for your FROM domain
- Ensure an accurate From: header
- Ensure an accurate send domain name
- Create a one-click unsubscribe option
- Include it in your email body
- Add it to the list-unsubscribe header
- Establish a process to guarantee that unsubscribe requests are addressed within 2 days
- Establish a system to monitor your spam complaint rate and keep it below 0.3%
New Technical Authentication Requirements
Start with SPF, DKIM and DMARC Requirements
Strengthen your email security with DMARC, SPF, and DKIM authentication practices. By authenticating your brand, you’ll gain recognition and a positive reception on Yahoo and Gmail platforms, ultimately leading to improved inbox placement.
SPF (Sender Policy Framework)
SPF, an email authentication standard, safeguards both senders and recipients from spam, spoofing, and phishing threats. Embedding an SPF record in your Domain Name System (DNS) establishes a public list of authorized senders permitted to send emails on behalf of your domain.
- For example, If you use an ESP like Klaviyo to send marketing and transactional emails, you’ll need to add Klaviyo’s sending servers as approved senders by configuring the SPF record.
How to authenticate: Create your SPF record, which should look something like this:
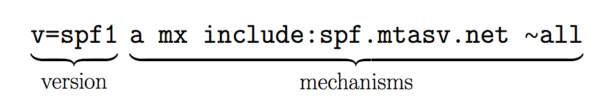
Pro Tip: Postmark App provides one of the most helpful guides we’ve found for adding an SPF record – https://postmarkapp.com/guides/spf
DKIM (Domain Keys Identified Mail)
DKIM enables domain owners to automatically add a ‘signature’ to emails originating from their domain. This cryptographic digital signature acts as a mathematical proof that the email truly originated from the claimed domain. Think of it in a similar way to how a signature on a check verifies the person who wrote the check.
How to authenticate: Include a DKIM header code (example below) in all your email sends.
v=1; a=rsa-sha256;
d=example.com; s=big-email;
h=from:to:subject;
bh=uMixy0BsCqhbru4fqPZQdeZY5Pq865sNAnOAxNgUS0s=;
b=LiIvJeRyqMo0gngiCygwpiKphJjYezb5kXBKCNj8DqRVcCk7obK6OUg4o+EufEbB
tRYQfQhgIkx5m70IqA6dP+DBZUcsJyS9C+vm2xRK7qyHi2hUFpYS5pkeiNVoQk/Wk4w
ZG4tu/g+OA49mS7VX+64FXr79MPwOMRRmJ3lNwJU=
Pro Tip: In Gmail, check an email’s header (including DKIM status) by clicking the three vertical dots in the upper right-hand corner of the email, then selecting ‘Show Original’ from the dropdown menu.
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication Reporting and Conformance)
DMARC doesn’t function as an email authentication protocol but serves as a policy checked by receiving mail servers prior to email delivery. It plays a crucial role in deciding the appropriate action when an email fails the authentication process.
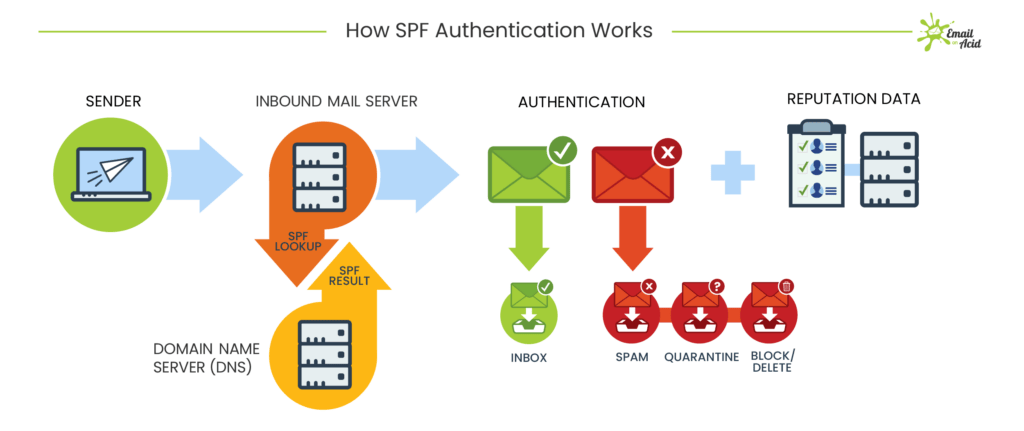
How to authenticate:
- Sender or domain owner establishes rules for authenticating emails sent from or on behalf of their domains.
- The sender configures their sending email servers and publishes the rules in DNS records.
- Receiving mail servers authenticate messages from the sender based on the published rules.
- Receiving email servers adhere to the rules and either deliver, quarantine, or reject the message.
Additional Technical Requirements
Valid PTR Records: PTR records, or Pointer Records, function as the reverse lookup in DNS. While DNS acts as the Internet’s phonebook, linking domain names with IP addresses through A Records when you enter a URL, PTR records operate in the opposite direction. They help identify a domain when given an IP address in a reverse DNS lookup.
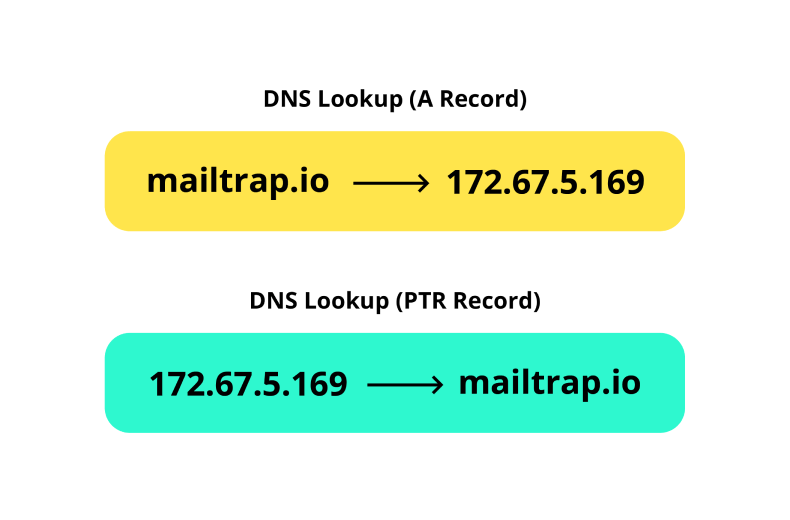
How to configure: Work with your site development team to establish a Reverse DNS zone. In DNS, a zone is a distinct segment of a domain namespace. The size of the zone is directly connected to the scale of your IP network.
Gmail’s “gmail.com” Policy: Gmail will quarantine emails impersonating “gmail.com” in the sending domain or Gmail From: headers if sent from anywhere other than a Google account.
- For example, sending an email from support@gmail.com, but with a different sender’s domain, is impersonating Gmail’s “From” headers. Sending an email from john.doe@gmail.com, but from a different sender’s domain, is impersonating “gmail.com” in the sending domain.
New User Complaint Requirements
Easy and Timely Unsubscription
Bulk senders are required to incorporate one-click unsubscribe options within the email body and a list-unsubscribe header. Additionally, these unsubscription requests need to be processed within two days according to the new requirements.
How to implement: Ensure that your unsubscribe process is a one-click process, and unsubscribed users are processed within 48 hours.
Spam Complaint Threshold
To tackle spam, Gmail and Yahoo are implementing a requirement for senders to keep their spam complaint rate below 0.3%. Going above this threshold might result in your emails getting blocked or directed to the bulk folder.
How to monitor: In addition to your ESP monitoring, we highly recommend configuring Google Postmaster as well as working with a trusted partner such as Inbox Monster.
What Happens if You Don’t Meet These Requirements?
It’s important to keep in mind that while these changes may seem daunting, they are designed to enhance email security, reduce spam, and improve the overall user experience — goals that benefit all parties involved.
Just keep in mind: If you fail to meet these requirements your deliverability rates could fall, and your email campaigns might be automatically flagged as spam by Gmail or Yahoo servers — an email marketers worst nightmare.
WITHIN’s email marketing services can guarantee that your email marketing program not only complies with these new requirements but also boosts open rates, engagement, and lead conversions. Send us a message to learn how.